
August 08, 2023
[Navigating Tractor Emissions Regulations | Part 1] A Guide to EU Stages and US Tiers

As a result of the increased focus on environmental sustainability, environmental distress resulting from agricultural operations is becoming more significant on a global scale. One of the biggest factors for agricultural pollution is exhaust gas emissions released by tractors and other farming equipment during fuel combustion. These include pollutant gasses like carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxide (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and hydrocarbons (HC).
Governments across the globe have implemented strict emission norms to address these emissions, and two major regulatory frameworks in this regard are the European Union (EU) Stages and the United States (US) tiers for non-road vehicles and machinery.
These frameworks establish specific standards and requirements for agricultural tractor emissions, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of agricultural activities. In recent years, there has been a progression in the prescribed norms and more and more stringent limits have been introduced (97/68/EC, 2010/22/EU, 2010/26/EU) limiting the emission of NOX, CO, PM and HC from engines.
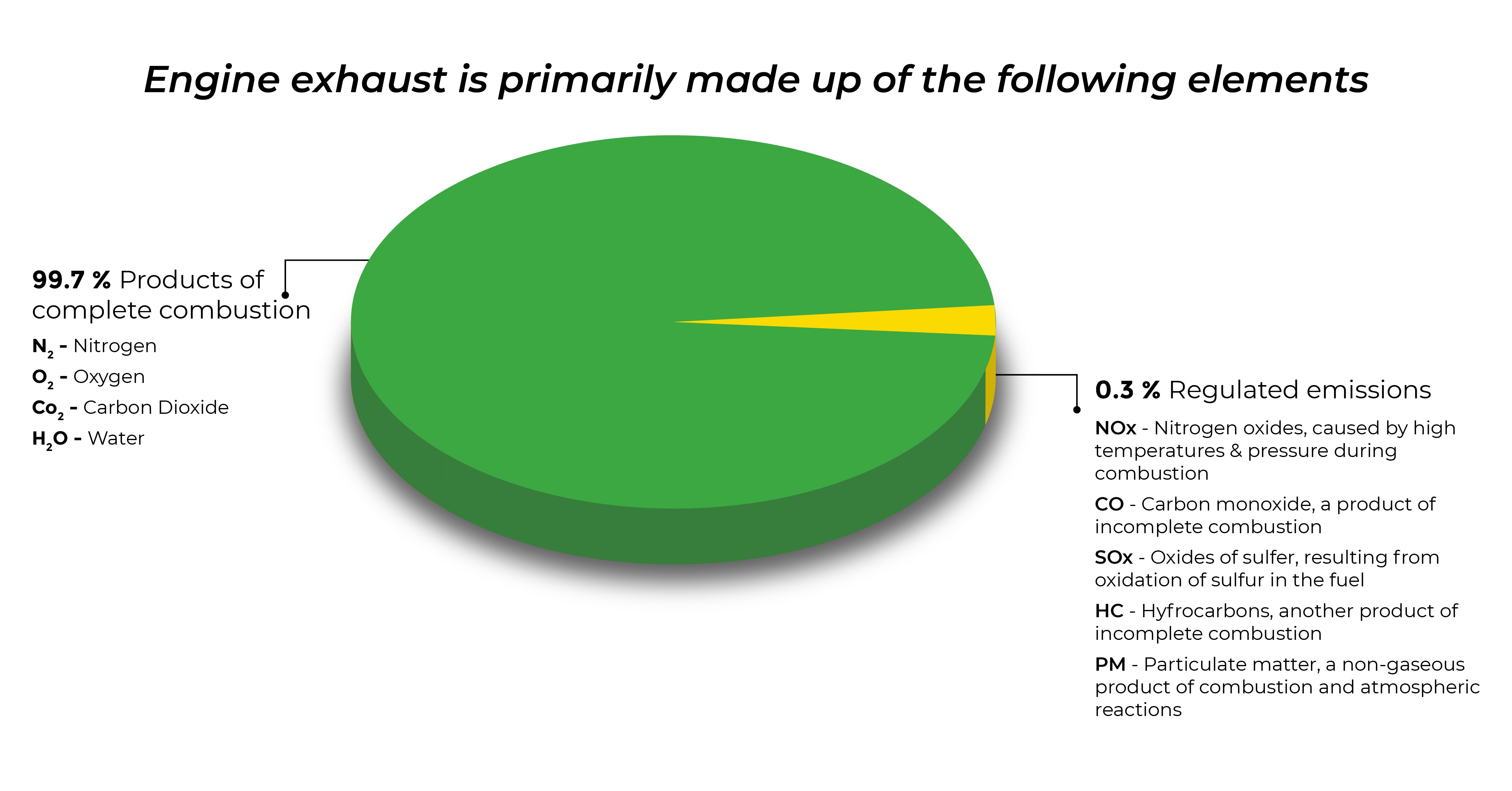 Decoding EU Stages and US Tiers
Decoding EU Stages and US Tiers
When it comes to environmental regulations and emissions standards, the EU and the US follow different approaches. Below is a comparison of these two systems to gain a deeper understanding of how each region tackles air pollution and promotes cleaner technologies.
| Aspect | EU Stages | US Tiers |
|---|---|---|
|
Governing Organization |
EU (European Union) |
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) |
|
Primary Focus |
PM and NOx emissions |
PM, NOx, HC, and CO emissions |
|
Other Regulated Pollutants |
Limited scope |
Wider scope |
|
Emission Limits |
Stricter limits for PM and NOx emissions |
Gradually tightening limits with each tier |
|
Testing Procedures |
A type-approval system with laboratory testing |
Laboratory testing and real-world testing |
|
Implementation Timeline |
Predefined deadlines for each stage |
No strict deadlines, focus on target dates |
|
Harmonization |
Applicable across EU member states |
Specific to the United States |
|
International Alignment |
Generally aligned with global standards |
May have unique requirements and variations |
John Deere’s Commitment to Meeting Different Regulations
John Deere takes its responsibility for emissions compliance very seriously. We have been working on reducing engine emissions since 1967 when John Deere first installed emissions testing equipment — years before governments recognized the need for regulations.
In 1996, John Deere launched a new breed of engines called PowerTech™ to meet U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and European Union (EU) Tier 1/Stage I emissions regulations. We built on this off-highway engine platform to meet emissions regulations for Tier 2/Stage II in 2001, Tier 3/Stage III A in 2006, Interim Tier 4/Stage III B in 2008, and Final Tier 4/Stage IV in 2013.
By integrating advanced engine technologies and exhaust after-treatment systems, John Deere’s Stage 5 Engine tractors are designed to meet major non-road emissions regulations worldwide, making them a reliable choice especially, for farmers in Southeast Asia and beyond.
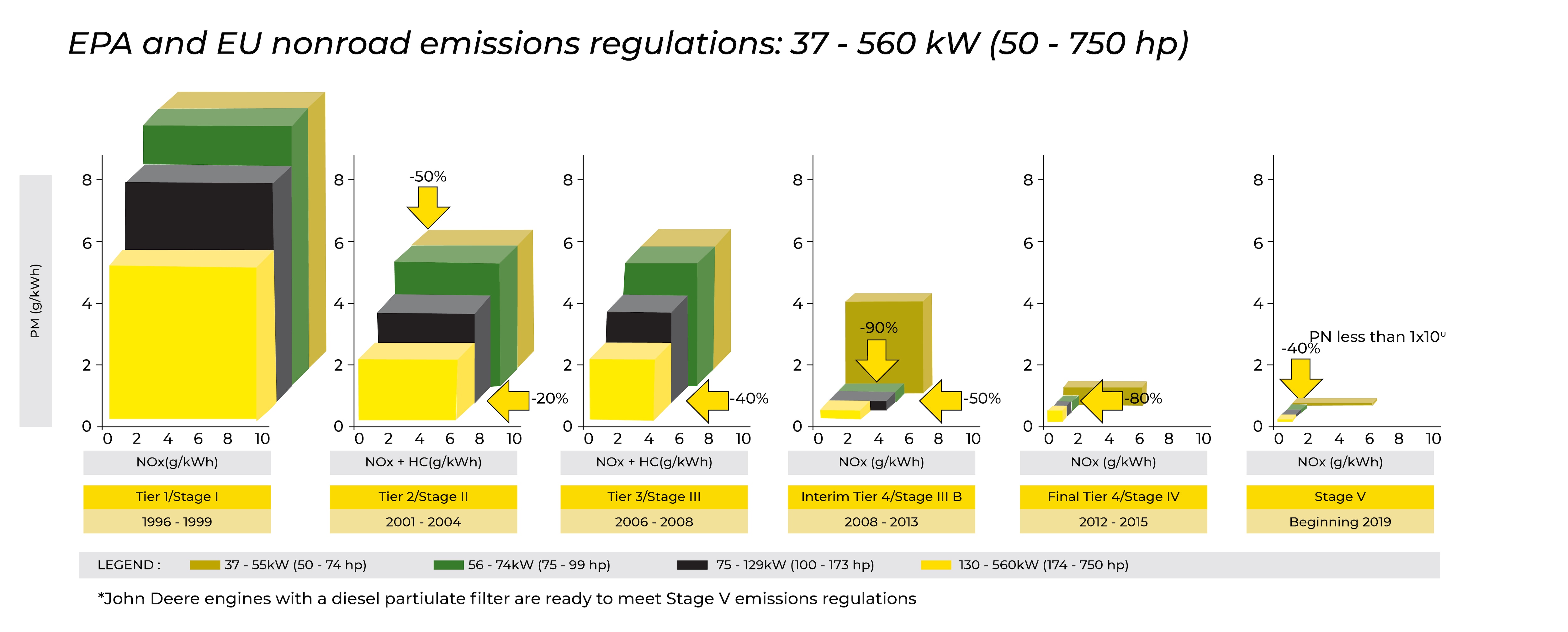
Understanding and adhering to tractor emission regulations is essential for farmers to mitigate their environmental impact. The EU Stages and US Tiers provide guidelines and standards to reduce emissions from agricultural machinery, promoting a more sustainable and eco-conscious agricultural industry. With the commitment of the world’s leading farming equipment companies like John Deere, farmers can rely on innovative and compliant equipment to ensure their contribution to a greener future.
Choose John Deere tractors, to contribute to building a sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
* For more information about John Deere’s Stage 5 Engine Tractors, you can contact your local John Deere dealers or leave your inquiry through our Contact us form.